You are here: / Home
High Capacity Pulse Tube Cooler

for Cryogenic High-Power Applications
Within the framework of the research project "Supraconducting High Current System for DC Applications", a high power cryocooler based on the pulse-tube (PT) principle was developed. The single-stage design has two pressure wave generators with a common drive, see Fig. 1. Unlike a classic PT cooler with orifice and buffer volume, the phase relation between pressure and mass flow can be fixed by the angle of rotation of the two pressure wave generators. This technique is called "active phase shift". This allows a much higher efficiency to be achieved, since the expansion energy at the warm end of the pulse tube is not dissipated but recuperated.
The cold head of this PT cryocooler is specially adapted to the application as a recooler / condenser. The cold surface is designed as a heat exchanger in order to be able to connect the media to be cooled directly to it. This enables optimum heat transfer between the internal thermodynamic process and the medium to be cooled, e. g. LN2. Due to its special design, the PT cryocooler requires no valves and no moving parts in the cold section. This ensures a long service life, high reliability and low maintenance.
This PT cryocooler (high power cryocooler) is particularly suitable for use as:
- Cooler for small condensers, e. g. for the condensation of O2, N2, H2, etc.
- Recooler for cryogenic cooling circuits with LN2 or Lar, e. g. for HTC (High Temperature Superconductor) applications
The advantages of the system are:
- High efficiency
- Long service life and reliability with low maintenance requirements
- Special system solution with heat exchanger and process connections integrated in the cold surface
- Adaptability of the cryocooler to various special requirements
- Adjustable cooling capacity via the revolution speed of the compressor
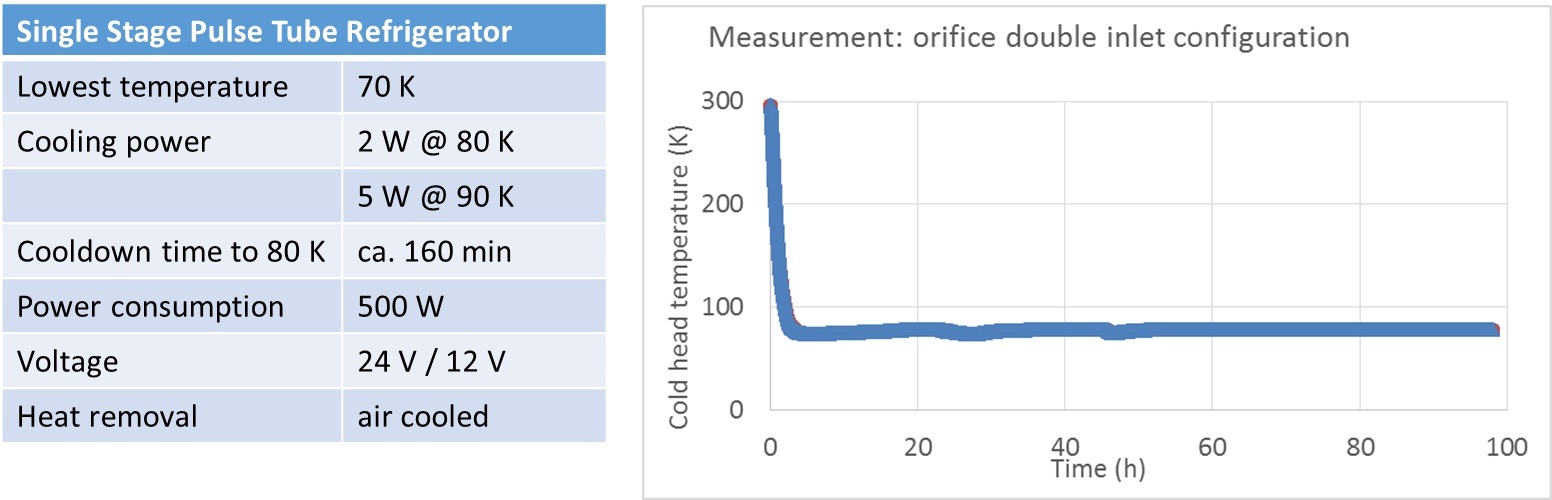
In the present configuration with the single-stage structure, a low temperature of 60 K is achieved. The cooling capacity is 300 W at 80 K. The temperature stability of the system was proven in an endurance test, see Fig. 2. Further modifications are planned to increase efficiency and cooling capacity. In addition, the pressure wave generators are to be further adapted in order to further reduce the dimensions of the system.
Wir suchen Kunden und Projektpartner für mögliche Weiterentwicklungen oder auch Adaptionen für spezielle Anwendungszwecke. Denkbar sind zum Beispiel ein kompakteres System oder eine Weiterentwicklung des derzeitigen Kühlers zu noch mehr Kälteleistung, tieferen Temperaturen und höherer Effizienz.
Further Projects
Intelligent innovative power supply for superconducting coils
Compact, powerful power supply with 4-quadrant converter
Multifunctional electronic modules for cryogenic applications
Electronic with less wiring effort - more than 100 sensors via one feedthrough
Certifiable connection types in cryogenics
Detachable and permanent connections, adhesive bond / form closure / force closure
Combined building and system simulation
Scientific analysis of thermodynamic processes in buildings and its systems