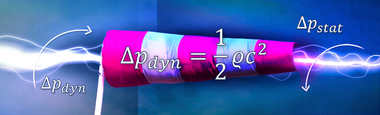In many areas centrifugal fans are used for conveying air. Depending on the installation situation and requirements, the use of a housingless fan, a so-called free-running impeller, can be feasabile. A typical application is, for example, the air conditioning unit (see Figure 1). A disadvantage is the functionally swirling discharge from the impeller. This may lead to poorer acoustics, more pressure loss and lower performance in downstream components such as filters, silencers or heat exchangers.

According to the state of the art, the swirl can be removed from the flow by various means. On the one hand, the use of a spiral housing is possible, on the other hand, the use of discharge guidevanes are possible. The volute casing contradicts the purpose of the free-running impeller and still has a high air speed at the outlet. Both the volute casing and the guide vanes can both help to convert the existing dynamic pressure from the impeller into usable static pressure, but neither is capable of transferring additional energy to the fluid.
Therefore, the task of this research project is to create a swirl-free outflow from an impeller using a new type of contra-rotating impeller. The mode of operation shown in Figure 2 is based on the speed triangles of the two counter-rotating impellers.
On the basis of a speed and volume flow dependent coordination of the two impellers with each other, a shock-free flow is achieved with the contra-rotating design of the second impeller and the relative speed w is further decelerated. Due to the existing pre-swirl, a swirl-free pressure reduction can be achieved despite the reduction in speed.


The following subtasks must be clarified in order to successfully deal with the topic:
- Design, tuning and optimization of the impellers
- Development of a suitable drive concept
- Reduction of leakage in the gap between the two impellers
- Optimization of the acoustic properties
- Development of a swirl detector for the control of the fan
The use of a contra-rotating centrifugal fan provides the following advantages:
- A swirl-free outflow for higher static efficiency, comparable to a housing or a guide vane
- Optimum flow to the downstream components from a thermodynamic and flow mechanics point of view
- Optimum efficiency by adjusting the speeds
- Greater performance with the same construction volume